Economic survey 2022 agriculture summary pdf download, Economic survey agriculture upsc, economic survey upsc
Introduction
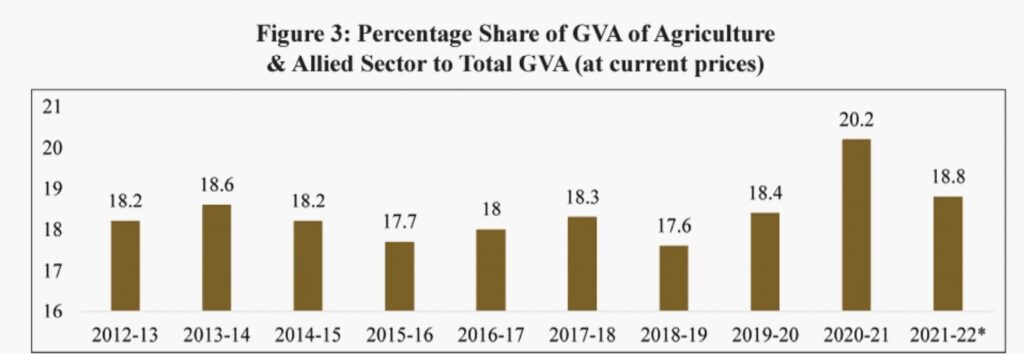
Agriculture sector, which is the largest employer of workforce, accounted for 18.8 per cent (2021-22) in Gross Value Added (GVA) of the country and registered a growth of 3.6 per cent in 2020-21 and 3.9 per cent in 2021-22.
The economic survey 2022 highlighted the importance of crop diversification and advocated gradual shift from the cultivation of water-intensive crops like sugarcane and paddy to cotton, horticulture, nutri-cereals, pulses and oilseeds.
Overall the positive growth in agriculture this can credited to the following factors –
- Good monsoon
- Enhanced credit availability measures by government
- Improved investments
- Improved Market infrastructure
- Promotion of infrastructure development in the agriculture sector
The Committee on Doubling Farmers’ Income (DFI, 2018) considers the dairy, livestock, poultry, fisheries and horticulture as engines of high growth and has recommended a focused policy with a concomitant support system.
Investment in Agriculture and allied sectors
The Gross Capital Formation (GCF) in agriculture and allied sectors relative to GVA in the sector has been showing a fluctuating trend .
The fluctuating trend can be attributed to the wide fluctuations in private investment in agriculture and allied sectors where the public sectors have remained stable.
New Food grain production record
As per the Fourth Advance Estimates for 2020-21, the total food-grain production in the country is estimated at a record 308.65 million tonnes which is 11.15 million tonnes higher than that during 2019-20.
The Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of major crops during the last six years (2015-2021) are:
Rice : 2.7%,
Wheat: 2.9%
Coarse cereals: 4.8%
Pulses: 7.9%
Oilseeds: 6.1%
Cotton: 2.8%
Oilseed Production
India is one of the major oilseeds growing countries in the world. The oilseed production in India has grown by almost 43 per cent from 2015-16 to 2020-21. However this growing production has not been able to meet our domestic demand and hence we import oilseeds form other countries. Currently India is the world’s second largest consumer and number one importer of vegetable oil.
Improving import and production of oil
Oil palm produces around 10 to 46 times more oil per hectare compared to other oilseed crops and has a yield of around 4 tons oil per ha. However, around 98 per cent of CPO is being imported.
In view of the persistently high import of edible oil, increase in oil production has been a priority for the Government.
Government has been promoting the production and productivity of oilseeds through the centrally sponsored scheme of National Food Security Mission: Oilseeds (NFSM-Oilseeds).
As of August, 2021, National Mission on Edible Oils – Oil Palm (NMEO-OP) has been launched to augment the availability of edible oil in the country by harnessing area expansion and through price incentives. It aims to cover an additional area of 6.5 lakh hectares for oil palm till 2025-26.
Sugarcane and Sugar sector in economic survey 2022 agriculture
India is the largest consumer and the second-largest producer of sugar in the world.
Average annual production of sugarcane is around 35.5 crore tonnes which is used to produce around 3 crore tonnes of sugar annually.
India has become a sugar surplus nation, since 2010-11, production has outstripped consumption except in 2016-17.
Some of the various measures taken by government to protect farmers
- Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP): Doubled in a span of 10 years
- Some state announces State Advised Price(SAP) , which is higher than FRP
- Cane Reservation Area: Mill owners to buy crop from farmers within a specified radius
To handle the surplus production and enhance liquidity of mills, the Government is incentivizing sugar mills to divert excess sugar cane/sugar to ethanol production, providing financial assistance for transport to sugar mills to facilitate export of sugar etc.
Minimum support price or Price policy
In the Union Budget 2018-19 had announced the predetermined principle to keep MSP at the level of one and half times the cost of production.
Based on this principle, the Government has announced the increase in MSP for all mandated kharif crops of the year 2021-22.The expected returns to farmers over cost of production is estimated to be highest in case of bajra (85 per cent).
Crop Diversification
The Doubling Farming Income Committee suggests that shifting some area from staple cereals to high value produce can lead to a sizable increase in the returns for farmers, this would also bring in water use efficiency and sustainability of soil health.
The existing cropping pattern is skewed towards cultivation of sugarcane, paddy and wheat which has led to depletion of fresh groundwater resources at an alarming rate in many parts of our country.
Crops Diversification Programme (CDP) is being implemented in the original green revolution states viz. Punjab, Haryana and Western UP as a sub scheme of Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) since 2013-14 to shift area under paddy cultivation towards less water requiring crops such as oilseeds, pulses, coarse cereals, nutri cereals, cotton, etc.
Agricultural Credit Economic survey 2022 agriculture
Government announced ₹ 2 lakh crore concessional credit boost to 2.5 crore farmers through Kisan Credit Cards (KCCs).
To address the credit needs of animal husbandry and fish farmers, the Government of India in 2018-19 extended the facility of KCC to fisheries and animal husbandry farmers to help them meet their working capital needs.
Water and Irrigation
The share of net irrigated area accounts for about 49 per cent of the total net sown area in the country and out of the net irrigated area, about 40 per cent is irrigated through canal systems and 60 per cent through groundwater.
The Ratio of annual ground water draft and net annual ground water availability in the country is 63 percent. This ratio signifies the rate of extraction of ground water.
The ratio is very high (more than 100 per cent) in the states of Delhi, Haryana, Punjab and Rajasthan.
Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh and UTs of Chandigarh and Puducherry falls in the medium category (Ratio:70-100).
Natural Farming
The main aim for promotion of Natural Farming is elimination of chemical fertilizers and pesticides usage and promotion of good agronomic practices. (Bharatiya Prakritik Krishi Paddhati Programme)
The scheme promotes on-farm biomass recycling with major stress on biomass mulching, use of on-farm cow dung-urine formulations, periodic soil aeration and exclusion of all synthetic chemical inputs.
Agricultural Marketing
Wholesale agricultural marketing is undertaken by the network of 6946 regulated wholesale markets, set up under the provision of respective State Agricultural Produce Market Committee (APMC) Act.
Government of India launched National Agriculture Market (e-NAM) Scheme in 2016 with the objective of creating online transparent competitive bidding system to facilitate farmers with remunerative prices for their produce.
As on 1st of December, 2021, 1000 mandis of 18 States and 3 UTs have been integrated with e-NAM platform.
Allied Sectors: Animal Husbandry & Dairying
Livestock Sector is an important subsector of agriculture in the Indian economy. It grew at a CAGR of 8.15 percent during 2014-15 to 2019-20 (at constant prices).
Livestock sector contributed 4.35 per cent of total GVA in 2019-20.
Dairy Sector
Dairy is the single largest agricultural commodity contributing 5 per cent of the national economy and employing more than 8 crore farmers directly.
India is ranked 1st in milk production contributing 23 per cent of global milk production.
Egg and Meat Production
According to FAOSTAT production data (2020), India ranks 3rd in Egg Production and 8th in meat production in the world.
Fisheries
India is the second largest fish producing country in the world accounting for 7.56 per cent of global production. It contributes about 1.24 per cent to the country’s GVA and over 7.28 per cent to the agricultural GVA.
- Fisheries sector has a double-digit average annual growth of 10.87 % since 2014-15.
- In terms of employment, the sector supports the livelihood of over 28 million people.
- To address the credit needs of fish farmers, KCC facility extended to fisheries.
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) launched for enhancing fish production.
Crop Residue Management
To support the efforts of the Governments to address air pollution and to subsidize machinery for
the farmers for in-situ management of crop residue, a new Central Sector Scheme on Promotion of
Agricultural Mechanization for In-Situ Management of Crop Residue in the States of Punjab, Haryana,
Uttar Pradesh and NCT of Delhi’ (CRM) for the period from 2018-19 to 2020-21 had been launched
with a total outlay of ₹ 1791.80 crore.
Mechanization
The penetration of powered machines in various farm activities is assessed in the range of 40 to
45 per cent (NABARD, 2018). To promote an inclusive growth of farm mechanization in the country, a Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM) was launched in the year 2014-15. Sale of tractors and power tillers may be used as an indicator of farm mechanization. Indian tractor industry is the largest in the world accounting for one-third of the total global production.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana (PMKSY)
Various components under the umbrella central sector scheme PMKSY, includes (i) Mega Food Parks, (ii) Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure, (iii) Infrastructure for Agro-processing Clusters, (iv) Creation of Backward and Forward Linkages (v) Creation / Expansion of Food Processing & Preservation Capacities, (vi) Operation Greens and (vii) Food Testing Laboratories.
TOP Scheme
Operation Greens Scheme was announced in the Union Budget for 2018-19 to promote Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs), agri-logistics, processing facilities and professional management for Tomato, Onion and Potato (TOP) crops.
Fortification of Rice and its Distribution
- The Government of India approved the Centrally Sponsored Pilot Scheme ‘Fortification of Rice and its Distribution under Public Distribution System’ for a period of 3 years beginning 2019-20.
- The Government has started distributing fortified rice under ICDS Scheme and PM Poshan schemes across the country during 2021-22 in an effort to fight malnutrition and micronutrient deficiencies among pregnant women, lactating mothers, children etc.
One Nation One Ration Card
Through this system migratory beneficiaries shall be able to access their food security entitlements
from any fair price shop (FPS) of their choice by using their same ration card after biometric/Aadhaar
authentication on electronic Point of Sale devices at the FPS.
Open Market Sale Scheme
- FCI on the instructions from the Government sells excess stocks out of Central Pool through Open Market Sale Scheme (Domestic) [OMSS (D)] in the open market from time to time at predetermined prices called reserve prices.
- Under the OMSS (D) 2020-21 policy, a special dispensation for supply of foodgrains is made to all the NGOs engaged in relief or running community kitchens for migrant labourers.
Food Subsidy
- The difference between the per quintal economic cost and the per quintal Central Issue Price (CIP) gives the quantum of per quintal food subsidy.
- The economic cost of wheat has increased from Rs 1908.32 per quintal in 2013-14 to ₹ 2993.80 per quintal in 2021-22.
- The economic cost of rice has increased from Rs 2615.51 per quintal in 2013-14 to ₹ 4293.79 per quintal in 2021-22.
- However, as a pro-poor measure, the CIPs for NFSA beneficiaries have not been revised since the commencement of the NFSA.
Ethanol Blended with Petrol (EBP) Program
The Government has now set 20% ethanol blending target for mixing ethanol with petrol to be achieved
by 2025. It is estimated that the blending target at 10 % would be achieved during 2022.
Fertilizers
- New Urea Policy 2015 has been notified with the objectives of maximizing indigenous production, promoting energy efficiency in production, and rationalizing subsidy burden on the government. Government has made it mandatory for all the domestic producers of urea to produce only neem coated urea.
- Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) Scheme where subsidy is provided on each grade of subsidized Phosphatic and Potassic(P&K) fertilizers depending upon its nutrient content.
Food Processing Sector
- Food Processing Industries (FPI) sector has been growing at an average annual growth rate of around 11.18 per cent.
- FPI is one of the major employment intensive segments having a share of 12.38 percent in the employment generated in all Registered Factory sector in 2017-18.
Download link for pdf – Here
Soil science jrf question paper – Link
Difference between truthfully and certified seed – Link
Key highlights of economic survey – pib link

